Project Description
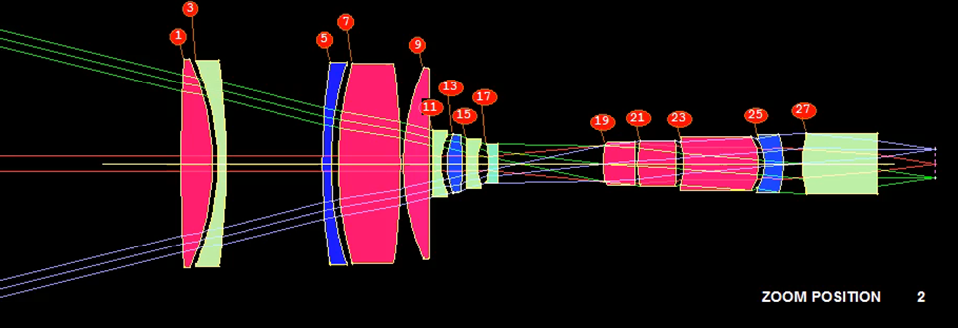
SYNOPSYS Synopsys Lens Design Software
- SYNOPSYS™ is one of the largest and most powerful lens design programs in the world, with features found nowhere else. It is also one of the easiest to use.
- The fastest lens optimization in the world. With its powerful PSD algorithm, SYNOPSYS can do in one second a job that takes other programs more than an hour.
- Friendly user interface, using simple commands as well as extensive dialogs and menus. A few keystrokes can often do the same thing as drilling down through a lengthy menu tree.
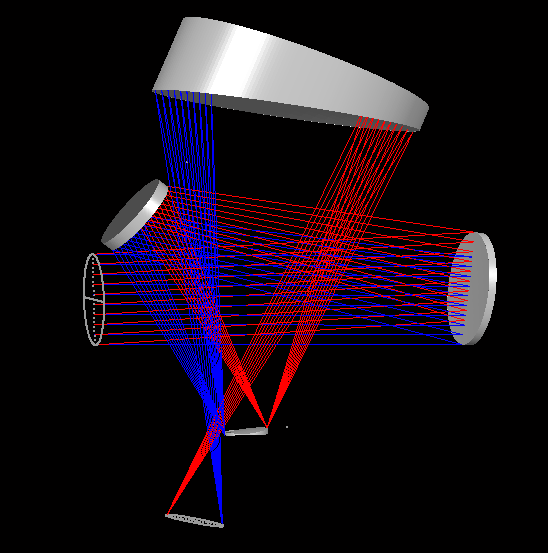
- A graphical interface, the SketchPad™, to visualize the lens and its image, with sliders to change almost any lens parameter while you watch the effect.
- Insert and delete elements or prisms, split and bend elements, and spin a 3-D image around, all in real time.
- Simple input can control every aspect of the lens or the image during optimization.
- Artificial Intelligence to create new commands or plot almost anything against anything.
- A CAM feature that lets you adjust the curve fit while you evaluate image quality, using a slider to smoothly zoom your lens.
- Statistical tolerancing to a specified confidence level, with Monte-Carlo verification and fabrication adjustment emulation.
- Extensive graphical output showing every aspect of the lens and its image.
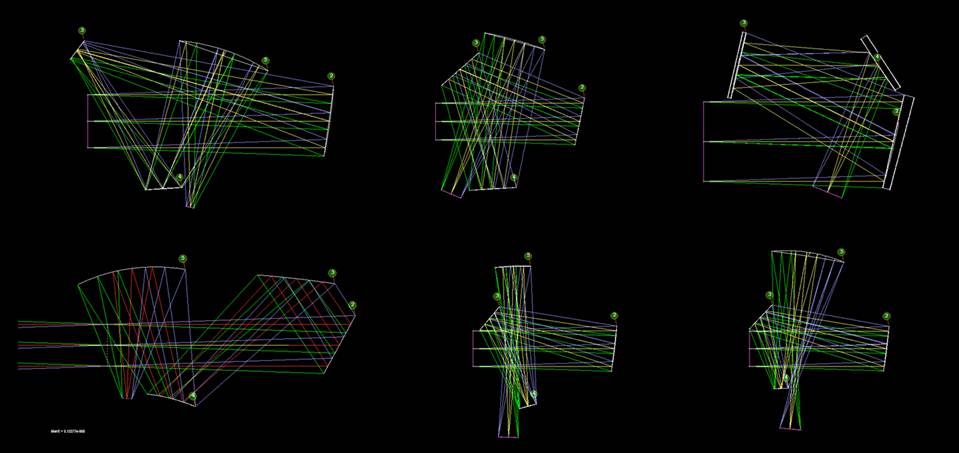
- Lens Optical Design
- Free Form Optical Design
- Reflector Optical Design
- Zoom Lens Optical System Design and ZSEARCH
- PSD Optimization
- Automatic Search(DSEARCH)
- Aberration and MTF Analysis
- Laser Beam Shaper Optical Design
- Artificial Intelligence
- Tolerancing Analysis
- Multi-Cores Parallel Computing
- Athermal Lens Design and GSEARCH
Optimization
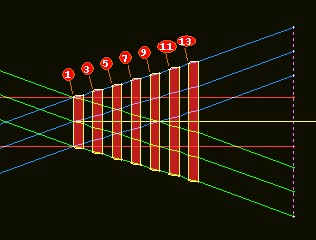
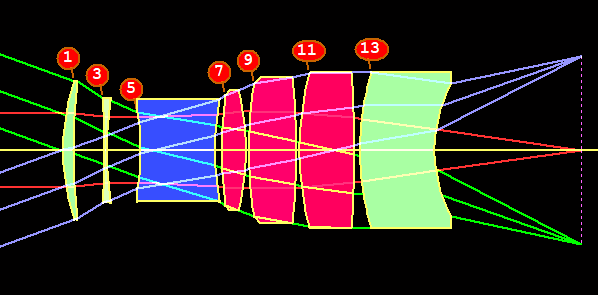
Free Form Surface
OS : Windows XP, 7, 8 or 10, 32-Bit / 64-Bit
HDD : 10G of free disk space
RAM : 4GB
CPU : Intel or AMD
- How do I use SYNOPSYS? What does it do?
– The Interface
– Editing and Changing Lens Data
– The Input File - What are the major differences between SYNOPSYS™ and Zemax™?
- What are the major differences between SYNOPSYS™ and Code-V™?
- What is the “PSD” optimization algorithm?
1 Entering a Lens File
2 Achromatizing the Lens
3 PSD Optimization
4 The Amateur Telescope
5 Improving a lens designed on another program
6 The Importance of Third-order Aberrations
7 The In and Out of Vignetting
8 The Apochromatic Objective
9 Tolerancing the Apochromatic Objective
10 A Near Infrared Objective
11 A Laser Beam Shaper, all spherical
12 A Laser Beam Shaper, with aspherics
13 Laser Beam Expander with Kinoform Lenses
14 A More Challenging Optimization Challenge
15 Real-World Development of a Lens
16 A Practical Camera Lens
17 An Automatic Real World Lens
18 What is a Good Pupil
19 Using DOEs in modern Lens Design
20 Designing aspheres for manufacturing
21 Designing an Athermal Lens
22 Using the SYNOPSYS Glass Model
23 Parametric optimization study and ray failure correction
24 Tolerance clocking and AI analysis of an image error
25 Tips and Tricks of a Power User
26 Putting it all Together
27 Understanding the Narcissus Effect
28 Understanding Artificial Intelligence
29 The Annotation Editor
30 Understanding Gaussian Beams
31 The Superachromat
32 Ghost Hunting
33 Importing a Zemax file
34 A 90-degree Eyepiece
35 Athermalizing an Infrared Telescope
36 Edges
37 Finding and Changing Lens Structure Automatically
38 A Zoom Lens from Scratch
39 Designing a free-form mirror system
40 An Aspheric Camera Lens from Scratch
41 Designing a very wide-angle lens
42 A Complex Interferometer
43 SpreadSheet or WorkSheet
44 Why doesnt SYNOPSYS use Coordinate Breaks
45 Using the Artificial Intelligence Feature for a Parametric Study
46 A Laser Diode Beam Converter
47 A 30X Zoom Lens
48. A Microlithography Lens from Scratch
2 Achromatizing the Lens
3 PSD Optimization
4 The Amateur Telescope
5 Improving a lens designed on another program
6 The Importance of Third-order Aberrations
7 The In and Out of Vignetting
8 The Apochromatic Objective
9 Tolerancing the Apochromatic Objective
10 A Near Infrared Objective
11 A Laser Beam Shaper, all spherical
12 A Laser Beam Shaper, with aspherics
13 Laser Beam Expander with Kinoform Lenses
14 A More Challenging Optimization Challenge
15 Real-World Development of a Lens
16 A Practical Camera Lens
17 An Automatic Real World Lens
18 What is a Good Pupil
19 Using DOEs in modern Lens Design
20 Designing aspheres for manufacturing
21 Designing an Athermal Lens
22 Using the SYNOPSYS Glass Model
23 Parametric optimization study and ray failure correction
24 Tolerance clocking and AI analysis of an image error
25 Tips and Tricks of a Power User
26 Putting it all Together
27 Understanding the Narcissus Effect
28 Understanding Artificial Intelligence
29 The Annotation Editor
30 Understanding Gaussian Beams
31 The Superachromat
32 Ghost Hunting
33 Importing a Zemax file
34 A 90-degree Eyepiece
35 Athermalizing an Infrared Telescope
36 Edges
37 Finding and Changing Lens Structure Automatically
38 A Zoom Lens from Scratch
39 Designing a free-form mirror system
40 An Aspheric Camera Lens from Scratch
41 Designing a very wide-angle lens
42 A Complex Interferometer
43 SpreadSheet or WorkSheet
44 Why doesnt SYNOPSYS use Coordinate Breaks
45 Using the Artificial Intelligence Feature for a Parametric Study
46 A Laser Diode Beam Converter
47 A 30X Zoom Lens
48. A Microlithography Lens from Scratch
